Understanding Heat Induction Sealing
Heat induction sealing is a widely used process in the packaging industry, primarily for sealing containers with lids or caps that have a foil liner. This method is valued for its ability to create a hermetic seal, ensuring product freshness, preventing leaks, and providing tamper evidence. To fully understand this process, it is essential to explore the components involved, the steps of the process, and the applications and benefits of heat induction sealing.
Components of Heat Induction Sealing
The heat induction sealing process involves several key components, each playing a crucial role in achieving a successful seal:
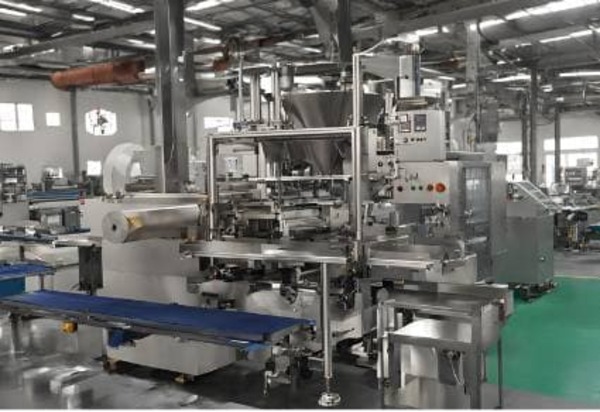
1. Induction Sealing Machine
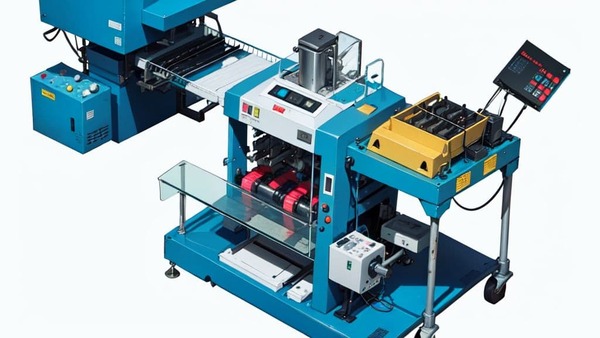
The induction sealing machine is the primary equipment used in this process. It generates an electromagnetic field that is crucial for heating the foil liner. These machines can vary in size and capacity, from small tabletop units to large industrial machines capable of handling high-volume production lines.
2. Container and Closure
The container, typically made of plastic or glass, and its closure, usually a cap, are essential components. The closure must be compatible with the induction sealing process, often containing a foil liner that will form the seal.
3. Foil Liner
The foil liner is a critical element that sits inside the cap. It usually consists of multiple layers, including a pulpboard backing, a wax layer, an aluminum foil layer, and a polymer film. The aluminum foil is the part that heats up and bonds to the container’s rim, creating the seal.
The Heat Induction Sealing Process
The process of heat induction sealing can be broken down into several steps, each crucial for ensuring a secure and effective seal:
1. Preparation
Before the sealing process begins, the container is filled with the product, and the cap with the foil liner is placed on top. The cap is typically screwed on or pressed down to ensure it is in contact with the container’s rim.
2. Induction Heating
Once the container and cap are prepared, they pass under the induction sealing machine. The machine generates an electromagnetic field that induces an electric current in the aluminum foil. This current heats the foil, causing the polymer film to melt and bond to the container’s rim.
3. Cooling and Bonding
After the foil is heated, the container is allowed to cool. During this cooling phase, the melted polymer solidifies, forming a strong bond between the foil and the container. This bond creates a hermetic seal that is both leak-proof and tamper-evident.
4. Quality Control
Quality control is an essential step in the heat induction sealing process. It involves checking the integrity of the seal to ensure it meets the required standards. This can be done through visual inspection, leak testing, or other methods depending on the application.
Applications and Benefits of Heat Induction Sealing
Heat induction sealing is used across various industries due to its numerous advantages. Here are some of the key applications and benefits:
Applications
This sealing method is prevalent in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals. It is used to seal bottles, jars, and other containers that require a secure closure to maintain product integrity.
Benefits
The primary benefits of heat induction sealing include:
- Preservation of Product Freshness: The hermetic seal prevents air and moisture from entering the container, preserving the product’s freshness and extending its shelf life.
- Leak Prevention: A secure seal prevents leaks, which is especially important for liquid products.
- Tamper Evidence: The seal provides a clear indication if the product has been tampered with, enhancing consumer safety and trust.
- Compatibility with Various Materials: Induction sealing can be used with a wide range of container materials, including plastics and glass.
- Efficiency: The process is quick and can be easily integrated into high-speed production lines, improving overall efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations
While heat induction sealing offers many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Material Compatibility: Not all container and cap materials are suitable for induction sealing. It is crucial to ensure compatibility to achieve a successful seal.
- Machine Calibration: Proper calibration of the induction sealing machine is necessary to achieve the correct heating and sealing parameters.
- Quality Control: Regular quality checks are essential to ensure the integrity of the seal and prevent product recalls.
- Initial Investment: The cost of induction sealing equipment can be high, which may be a consideration for smaller operations.
In conclusion, heat induction sealing is a vital process in the packaging industry, offering numerous benefits in terms of product preservation, safety, and efficiency. By understanding the components, process, and applications, businesses can effectively implement this sealing method to enhance their packaging operations.





