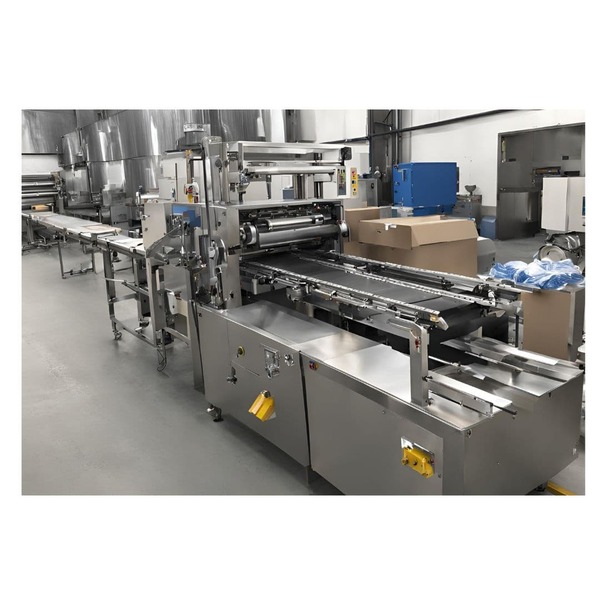
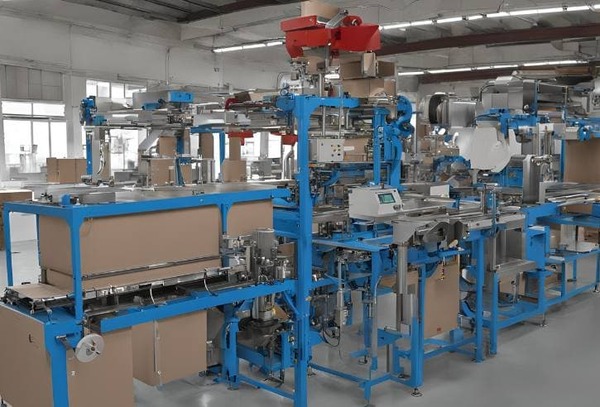
Introduction
Commercial vacuum sealers are indispensable tools in various industries, renowned for their ability to preserve products by removing air from packaging. This technology plays a crucial role in extending shelf life, maintaining product quality, and ensuring safety during storage and transportation. By creating an airtight environment, vacuum sealers inhibit the growth of aerobic bacteria and prevent oxidation, which can degrade products over time. Industries ranging from food processing to electronics rely on these machines to protect their goods. The integration of vacuum sealing with equipment like a big bag packing machine enhances efficiency in bulk packaging operations.
The Science Behind Vacuum Sealing
At the core of vacuum sealing is the removal of atmospheric air from the package, which contains oxygen—a key contributor to spoilage and degradation. Oxygen facilitates the growth of microorganisms and leads to oxidation reactions that can spoil food, corrode metals, and deteriorate pharmaceuticals. By evacuating air, vacuum sealers reduce the oxygen levels within the package to minimal amounts, significantly slowing down these detrimental processes.
The process involves placing the product in a packaging material, typically a plastic pouch or bag, and using the vacuum sealer to extract the air. The machine then seals the package, usually through heat sealing methods, to prevent air from re-entering. The result is a tightly sealed package that conforms closely to the product, offering protection and extending its usable life.
Components of Commercial Vacuum Sealers
Understanding the components of a commercial vacuum sealer provides insight into its functionality and efficiency. Key components include:
Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump is the heart of the machine, responsible for removing air from the packaging chamber. High-quality pumps can achieve lower atmospheric pressures, resulting in better vacuum levels. Pumps are typically categorized into rotary vane pumps, liquid ring pumps, or dry vacuum pumps, each with its own advantages based on the application.
Sealing Bar
The sealing bar applies heat to the packaging material to create a secure seal after air removal. Precision in temperature control is vital to ensure strong seals without damaging the packaging material. Advanced machines feature adjustable sealing times and temperatures to accommodate different packaging materials and thicknesses.
Control Panel
Modern vacuum sealers come with digital control panels that allow operators to set various parameters like vacuum time, sealing time, and cooling time. Some models include programmable settings for different products, enhancing efficiency and consistency in operations.
Chamber or Nozzle System
Depending on the type, vacuum sealers may have a chamber where the entire package is placed, or use a nozzle system for external bags. Chamber systems are typically used for liquids and powders, as they prevent product loss during air extraction.
Types of Commercial Vacuum Sealers
Commercial vacuum sealers are categorized based on their design and application. The main types include:
Chamber Vacuum Sealers
Chamber vacuum sealers are designed with an enclosed chamber where the product and packaging are placed. Air is removed from the entire chamber, ensuring a consistent vacuum level. These machines are ideal for liquid-rich foods and are widely used in food processing industries. The integration with a big bag packing machine can enhance packaging speed for bulk products.
External Vacuum Sealers
External vacuum sealers remove air by clamping the end of the bag and extracting air without enclosing the entire package. They are suitable for solid products and are often used in retail settings. While generally less expensive than chamber models, they may not achieve the same vacuum levels and are less suitable for liquids.
Roll Stock Vacuum Sealers
These high-speed machines use rolls of packaging material to form bags around the product, vacuum seal them, and then cut them to size. They are commonly used in large-scale operations where speed and efficiency are critical, such as in automated food packaging lines.
Applications in Different Industries
Commercial vacuum sealers are versatile and find applications across various industries:
Food Industry
In the food industry, vacuum sealing is essential for preserving meats, cheeses, vegetables, and prepared meals. By preventing microbial growth and oxidation, products remain fresh longer, reducing waste and ensuring safety. Vacuum sealing is also used in sous-vide cooking techniques, where food is cooked in its sealed package at precise temperatures.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical products often require protection from moisture and oxygen to maintain efficacy. Vacuum sealing provides a controlled environment that extends the shelf life of medications and protects sensitive compounds. The precision of vacuum sealers ensures compliance with strict industry regulations.
Electronics
Electronics are susceptible to damage from moisture and static electricity. Vacuum sealing electronic components prevents corrosion and protects against environmental factors during shipping and storage. It is a critical step in the supply chain for delicate and high-value electronic parts.
Advantages of Using Commercial Vacuum Sealers
The adoption of commercial vacuum sealers offers numerous benefits:
- Extended Shelf Life: By eliminating air, products remain fresh for longer periods, reducing spoilage and waste.
- Product Protection: Vacuum sealing safeguards products from physical damage, moisture, and contaminants.
- Space Efficiency: Vacuum-sealed packages are more compact, optimizing storage space and reducing shipping costs.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Clear packaging showcases the product, appealing to consumers and aiding in marketing efforts.
- Compliance: In industries with strict regulations, vacuum sealing ensures products meet safety and quality standards.
Integration with Packaging Systems
Commercial vacuum sealers are often integrated with other packaging systems to streamline operations. Combining a vacuum sealer with a big bag packing machine enables efficient handling of bulk products. This integration allows for automated feeding, weighing, vacuum sealing, and labeling of large packages, which is essential in industries like agriculture and chemicals where products are shipped in bulk.
Advanced systems may include conveyors, robotic arms, and sensors that further automate the packaging process. These systems improve productivity, reduce labor costs, and enhance consistency in packaging quality.
Technological Advancements
Recent technological developments have enhanced the capabilities of commercial vacuum sealers:
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
MAP involves replacing the air inside the package with a specific gas mixture, such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, to further extend shelf life. Vacuum sealers equipped with gas flushing capabilities can perform MAP, which is especially useful in packaging delicate food products that might be crushed by full vacuum pressure.
Sensor Integration
Modern machines incorporate sensors that monitor vacuum levels, seal integrity, and temperature. These sensors provide real-time feedback and alerts, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of packaging failures. Data collected can be used for quality control and process optimization.
Automation and Connectivity
Automation of vacuum sealing processes reduces manual intervention, increasing throughput and efficiency. Connectivity features enable machines to be integrated into larger production management systems, allowing for centralized control and monitoring.
Considerations for Selecting a Commercial Vacuum Sealer
Choosing the right vacuum sealer requires evaluating specific operational needs:
- Product Type: The nature of the product—solid, liquid, powder—impacts the choice of machine. Chamber sealers are preferable for liquids and powders.
- Packaging Volume: High-volume operations may require industrial-grade machines with higher throughput capabilities.
- Integration Needs: Consider whether the sealer needs to integrate with existing equipment, such as a big bag packing machine, for seamless operations.
- Packaging Material: The type and thickness of packaging materials dictate the sealing specifications required.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industries like pharmaceuticals may require machines that meet specific regulatory standards for cleanliness and validation.
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of vacuum sealers:
Regular Cleaning
Keeping the machine clean prevents contamination, especially in food and pharmaceutical applications. Cleaning routines should follow manufacturer guidelines and industry regulations.
Routine Inspection
Regularly inspecting components like the sealing bar, gaskets, and vacuum pumps helps identify wear and prevent breakdowns. Replacing worn parts promptly maintains sealing integrity.
Operator Training
Ensuring that operators are properly trained in using the equipment enhances efficiency and reduces the risk of errors. Training should cover machine operation, troubleshooting, and safety protocols.
Scheduled Maintenance
Following a scheduled maintenance program, often provided by the manufacturer, helps in keeping the machine running optimally. This may include oil changes for vacuum pumps and calibration of controls.
Challenges and Solutions
While commercial vacuum sealers offer numerous benefits, users may encounter challenges:
Packaging Material Compatibility
Not all packaging materials are suitable for vacuum sealing. Materials must have low oxygen permeability and be heat-sealable. Working with suppliers to select the appropriate materials is essential.
Product Crushing
Delicate products may be damaged by the vacuum pressure. Implementing MAP or adjusting the vacuum level can mitigate this issue, preserving product integrity.
Machine Downtime
Unexpected machine downtime can disrupt production schedules. Investing in reliable equipment, maintaining spare parts inventory, and having access to technical support reduces downtime risks.
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is increasingly important in packaging operations:
Using recyclable or biodegradable packaging materials can reduce environmental impact. Some vacuum sealers are compatible with eco-friendly materials, though these may require specific sealing parameters. Additionally, efficient machines consume less energy and contribute to sustainability goals.
Future Trends
Innovation continues to drive the evolution of commercial vacuum sealers:
Smart Technologies
Integration of IoT and smart sensors allows for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. Machines can self-diagnose issues and optimize performance, leading to higher efficiency and reduced downtime.
Customization and Flexibility
As consumer demands diversify, the need for flexible packaging solutions grows. Vacuum sealers that can handle various package sizes and materials enable companies to adapt quickly to market changes.
Sustainability Initiatives
Developments in sustainable packaging materials and energy-efficient machines will continue to be a focus. Companies are seeking solutions that balance performance with environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Commercial vacuum sealers are vital assets in modern packaging operations, offering solutions that extend product shelf life, ensure quality, and enhance efficiency. Understanding how they work and their integration with systems like a big bag packing machine enables businesses to optimize their packaging processes. With ongoing advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability, vacuum sealing will continue to evolve, meeting the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Selecting the right equipment, maintaining best practices, and staying abreast of industry trends positions companies to leverage the full benefits of commercial vacuum sealers.